Introduction
Contents
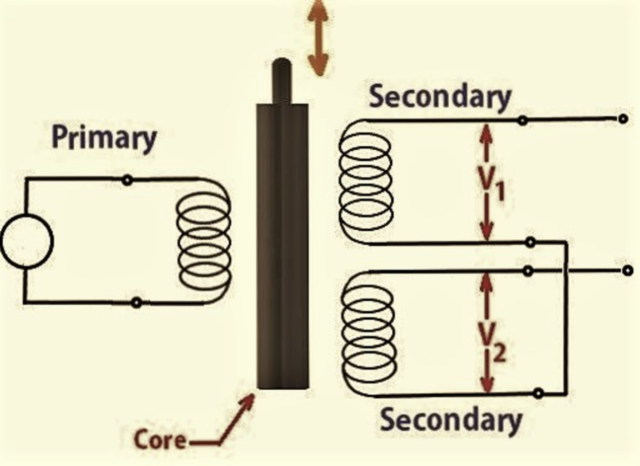
LVDT sensors are a type of electro-mechanical transducer. The working principle of LVDTs is mutual induction. They are used for converting mechanical or rectilinear motion into electrical signals. The use of LVDT inductive transducers is the most widely spread. This type of inductive transducer is called a Linear Variable Differential Transformer because the output of the transformer across the secondary (coil?) is differential. The sensors work on the principle of the transformer. The LVDTs’ sensors are electromagnetic sensors that are useful in measuring displacement. The readings of LVDT sensors are more accurate compared to other types of inductive transducers. LVDT sensors can measure the displacement from a millionth of an inch to an inch and position up to 20 inches.
Important features of LDTV sensors include frictionless operations, high resolution, an infinite life span, damage resistance, sensitivity to only one axis, robustness, null point repeatability, output accuracy and fast dynamic responses.
Accuracy Rate of LVDTs
LVDTs have infinite resolution, thus giving measurements of high accuracy. The accuracy of LVDT sensors is in the range of <.001 inches. The accuracy is controlled mechanical system design and signal conditioning electronics. In case of measuring the rate of thermal expansion of the components on which the LVDT sensors are core are mounted because any type of drift has a direct impact on output signals .
Advantages of LVDTs
LVDT sensors are the most preferred type of electromagnetic transducers because of their high resolution, accuracy, sensitivity, and linearity, thus providing ruggedness and frictionless operation. LVDT sensors are naturally frictionless as the uniaxial moving core does not touch the inner side of the tube. The frictionless property of the LVDT makes it the most reliable inductive transducer. Linear Variable Differential Transformers (LVDT sensors) help find precise position due to their high accuracy. The absence of rotation or sliding motion completely seals the LVDT, shielding it from environmental effects. When shut down, the LVDT shows the same measurements when restarted without losing any information regarding position.
Once properly configured, the LVDT sensors do not float that omit noise issue and make them repeatable as well as reproducible . LVDT sensors contain low physical phenomena and excellent repetition. An LVDT’s core uses a linear motion along one axis (uniaxial), in case any other movement like rotation along the axis has no impact on the measurements. If properly used, the LVDT sensor has an infinite life span. The lack of electronics in LVDT sensors makes them suitable for working in low-temperature environments (up to 1200oF temperature). LVDT sensors have high resolution, which makes them capable of calculating the tiniest movements with great precision.
Types of LVDT sensors
Different types of LVDT sensors are useful for various purposes: Captive Armature LVDT sensors have low resistance assemblies that prevent incorrect arrangements, Unguided Armature LVDTs provide very high resolution so they are useful where the measurement of small displacement is required. Force Extended Armatures are useful in robotics and avionics. Therefore, in order to choose the type of LVDT, some specifications are essential.
Applications of LVDT sensors
Linear Variable Differential Transformers or LVDT sensors have a number of advantages including:
- LVDTs are applicable in calculating dislocation from millimeters to centimeters
- LVDTs are the main transducers that convert dislocation into electrical signals
- LVDT sensors can work as secondary transducers
- They are not only for measuring displacement, but they can also measure pressure, force, load, and weight. LVDT sensors are useful in the measurement of dollar bill thickness in ATMs
- The sensors are useful for testing moisture in the soil
- In factories, LVDT sensors are useful for pills manufacturing
- In robotics, the LVDT sensors work as robot cleaners
- The sensors are important for brain probing purposes in medical devices
- LVDTs have multiple applications in power turbines, aircraft/ satellite and automation purposes
- As the LVDT sensor provides accurate position, it is helpful in sub-sea and ocean measurements for generating power in aerospace
- LVDTs provide automation in industries
- LVDT sensors are used in data acquisition systems for fast and accurate data acquisition
- LVDT sensors have signal noise reduction, making them useful in weighing apparatus for measuring mass
- LVDT sensors have practical applications in irrigational scheduling. LVDT sensors are sensitive to plant water stress. Therefore, they can determine the change in stem diameter due to the changes in plant water stress according to the seasons
- LVDT sensors have many applications in the field of civil engineering as they measure all physical quantities in engineering applications and industries
FAQs
Q1: What does LVDT stand for?
Ans 1: LVDT stands for Linear Variable Differential Transformer.
Q2: Is an LVDT an active or a passive transducer?
Ans 2: A Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) is an example of a passive transducer. With its response to environmental stimuli, it causes changes in passive electrical quantities like capacitance, resistance etc.
Q3: What is the accuracy of LVDT sensors?
Ans 3: LVDT sensors have a high accuracy since they have a resolution of <.001 inches.